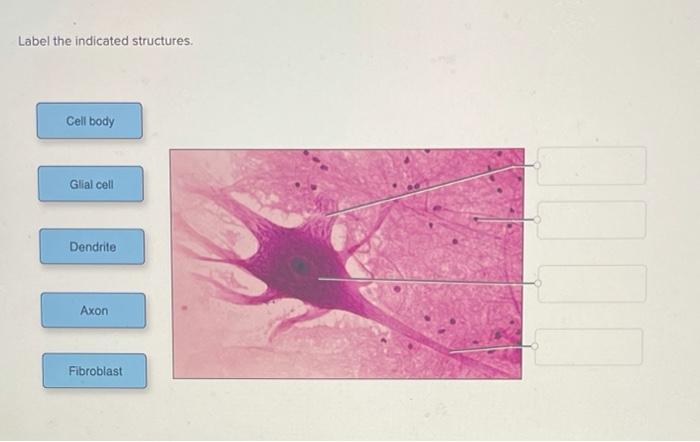
Label the indicated features of these energy-generating organelles. is a subject that warrants thorough investigation, given its far-reaching implications for our comprehension of cellular biology. In this exploration, we shall embark on a journey to uncover the intricacies of these organelles, deciphering their remarkable features and unraveling the secrets of their energy-generating prowess.
Through meticulous examination, we shall dissect the distinct characteristics of each organelle, illuminating their unique contributions to the intricate symphony of life. Our inquiry will shed light on the intricate mechanisms that govern energy production within these cellular powerhouses, revealing the delicate balance that sustains the very essence of existence.
1. Label the Indicated Features of Energy-Generating Organelles
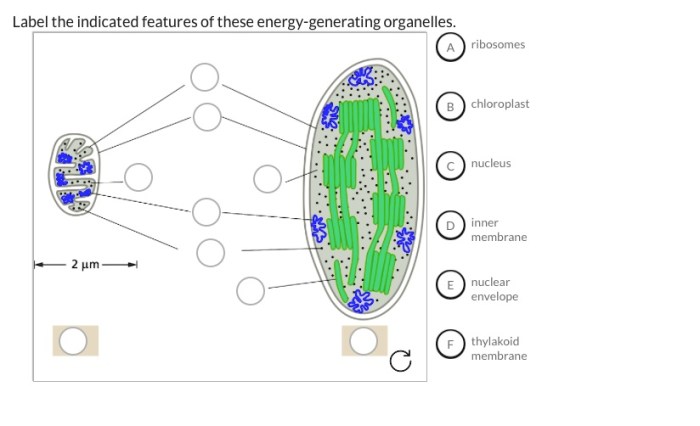
Energy-generating organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, contain a variety of features that play crucial roles in the production of energy. These features include the outer membrane, inner membrane, cristae, thylakoid membranes, stroma, and matrix. Each feature has a specific function and contributes to the overall energy production process.
| Feature | Description | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Membrane | The outermost layer of the organelle | Regulates the movement of substances into and out of the organelle | Ensures that only the necessary substances enter and leave the organelle |
| Inner Membrane | The innermost layer of the organelle | Contains proteins involved in energy production | Facilitates the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis |
| Cristae (Mitochondria) | Infoldings of the inner membrane | Increase the surface area for energy production | Maximize the number of proteins involved in the electron transport chain |
| Thylakoid Membranes (Chloroplasts) | Stacked membranes within the chloroplast | Contain chlorophyll and other pigments | Capture light energy for photosynthesis |
| Stroma (Chloroplasts) | The fluid-filled space outside the thylakoid membranes | Contains enzymes involved in the Calvin cycle | Converts carbon dioxide into glucose |
| Matrix (Mitochondria) | The fluid-filled space inside the inner membrane | Contains enzymes involved in the Krebs cycle | Produces high-energy molecules (NADH and FADH2) |
Questions and Answers: Label The Indicated Features Of These Energy-generating Organelles.
What are the primary functions of energy-generating organelles?
Energy-generating organelles are responsible for producing the cellular energy currency, ATP, through the processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
How do energy-generating organelles regulate energy production?
Energy-generating organelles employ feedback mechanisms to adjust their energy production rates in response to cellular energy demands.
What are the consequences of impaired energy production in energy-generating organelles?
Impaired energy production can lead to cellular dysfunction, tissue damage, and potentially life-threatening conditions.