Art-labeling activity anatomy and histology of the pancreas – Embark on a captivating journey into the intricate world of the pancreas through an art-labeling activity that unveils its anatomical structures and histological components. This activity invites you to explore the depths of this vital organ, providing an immersive learning experience that illuminates its complexities.
The pancreas, a glandular organ nestled within the abdominal cavity, plays a pivotal role in digestion and hormone regulation. Its unique anatomy and cellular composition endow it with the ability to secrete enzymes that aid in nutrient breakdown and produce hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which orchestrate blood sugar balance.
Anatomical Structures of the Pancreas: Art-labeling Activity Anatomy And Histology Of The Pancreas
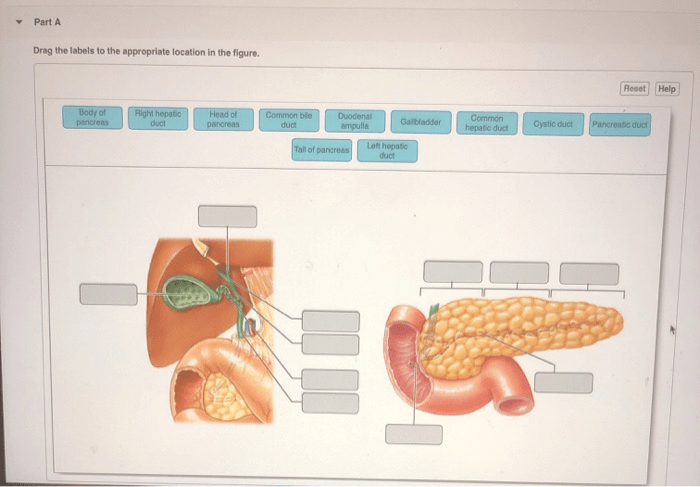
The pancreas is a glandular organ located in the abdominal cavity. It is approximately 15-25 cm in length and weighs around 100-150 grams. The pancreas has a head, body, and tail, with the head located on the right side, the body in the middle, and the tail on the left side.
The pancreas is located behind the stomach and is closely associated with the duodenum, liver, and spleen.
Head of the Pancreas
- The head of the pancreas is the widest part of the organ and is located on the right side.
- It is C-shaped and wraps around the duodenum.
- The head of the pancreas contains the uncinate process, which is a small projection that extends posteriorly.
Body of the Pancreas
- The body of the pancreas is the middle portion of the organ and is located between the head and the tail.
- It is relatively narrow and is located behind the stomach.
- The body of the pancreas contains the hilum, which is a depression on the posterior surface of the pancreas where the pancreatic duct and blood vessels enter and exit the organ.
Tail of the Pancreas, Art-labeling activity anatomy and histology of the pancreas
- The tail of the pancreas is the narrowest part of the organ and is located on the left side.
- It is located near the spleen and is often in contact with the left kidney.
- The tail of the pancreas contains the splenic process, which is a small projection that extends towards the spleen.
Relationship to Surrounding Organs
- The pancreas is located behind the stomach and is closely associated with the duodenum, liver, and spleen.
- The head of the pancreas is located on the right side of the duodenum and wraps around it.
- The body of the pancreas is located behind the stomach and is in contact with the left kidney.
- The tail of the pancreas is located near the spleen and is often in contact with it.
Histology of the Pancreas
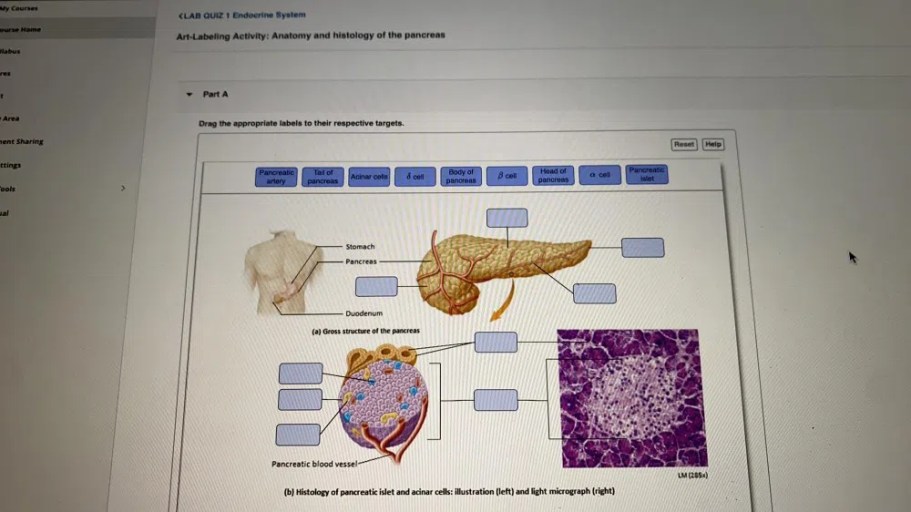
The pancreas is a compound gland with both exocrine and endocrine functions. The exocrine pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes that help to digest food. The endocrine pancreas produces hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, which help to regulate blood sugar levels.
Cellular Components of the Pancreas
- The pancreas is composed of several different types of cells, including acinar cells, ductal cells, and islet cells.
- Acinar cells are the most abundant cell type in the pancreas and are responsible for producing pancreatic juice.
- Ductal cells line the ducts of the pancreas and help to transport pancreatic juice to the duodenum.
- Islet cells are clusters of cells that are responsible for producing hormones.
Organization of the Pancreas
- The pancreas is organized into lobules, which are small, round structures that are surrounded by connective tissue.
- Each lobule contains several acini, which are clusters of acinar cells.
- The acini are connected to ducts, which transport pancreatic juice to the duodenum.
- The islet cells are located within the lobules and are not connected to the ducts.
Function of the Pancreas
- The pancreas plays a vital role in digestion and metabolism.
- The exocrine pancreas produces pancreatic juice, which contains enzymes that help to digest food.
- The endocrine pancreas produces hormones, such as insulin and glucagon, which help to regulate blood sugar levels.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of the pancreas?
The pancreas is responsible for producing enzymes that aid in digestion and hormones that regulate blood sugar levels.
What are the main anatomical structures of the pancreas?
The pancreas consists of a head, body, and tail, with the head located near the stomach and the tail extending towards the spleen.
What are the different cell types found in the pancreas?
The pancreas contains acinar cells that produce digestive enzymes, ductal cells that line the ducts, and islet cells that secrete hormones.