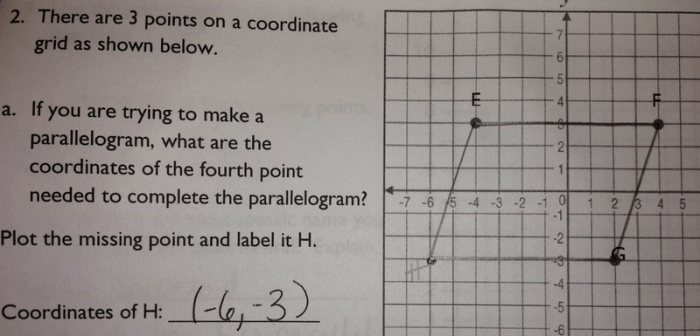Triangle abc is shown on the coordinate plane – Triangle ABC, gracing the coordinate plane, invites us to delve into a realm of geometric wonders. With its vertices precisely plotted, this triangle serves as a canvas for exploring concepts of length, area, angles, and transformations.
Unraveling the intricacies of Triangle ABC, we embark on a journey to uncover its hidden properties and relationships, promising a blend of mathematical rigor and geometric intrigue.
Overview
Triangle ABC is a triangle on the coordinate plane. The coordinate plane is a two-dimensional space with two axes: the x-axis and the y-axis. The x-axis is horizontal, and the y-axis is vertical. The origin, where the x-axis and y-axis intersect, is the point (0, 0). The coordinates of a point are the ordered pair (x, y), where x is the horizontal distance from the origin and y is the vertical distance from the origin.
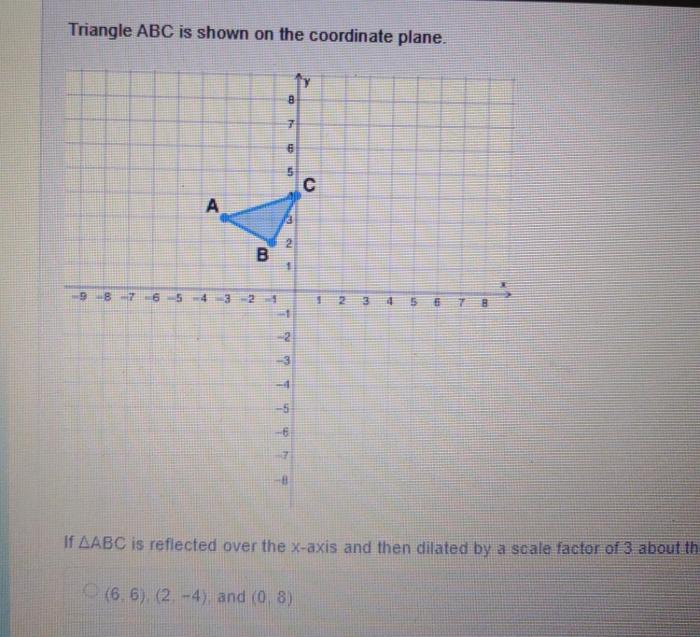
Triangle ABC is shown on the coordinate plane below.

Coordinates of the Vertices
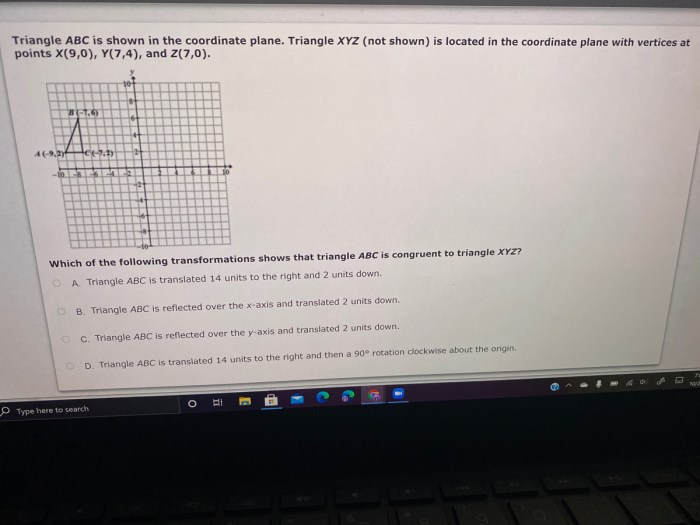
The vertices of Triangle ABC are A(2, 3), B(6, 1), and C(4, 5). The following table shows the coordinates of each vertex and the quadrant in which it lies.
| Vertex | Coordinates | Quadrant |
|---|---|---|
| A | (2, 3) | I |
| B | (6, 1) | I |
| C | (4, 5) | I |
Side Lengths and Slopes
The side lengths of Triangle ABC are:
- AB = sqrt((6 – 2)^2 + (1 – 3)^2) = sqrt(16 + 4) = sqrt(20) = 2sqrt(5)
- BC = sqrt((4 – 6)^2 + (5 – 1)^2) = sqrt(4 + 16) = sqrt(20) = 2sqrt(5)
- CA = sqrt((2 – 4)^2 + (3 – 5)^2) = sqrt(4 + 4) = sqrt(8) = 2sqrt(2)
The slopes of the sides of Triangle ABC are:
- m(AB) = (1 – 3) / (6 – 2) = -1
- m(BC) = (5 – 1) / (4 – 6) = 2
- m(CA) = (3 – 5) / (2 – 4) = 1
The following table shows the side lengths and slopes of the sides of Triangle ABC.
| Side | Length | Slope |
|---|---|---|
| AB | 2sqrt(5) | -1 |
| BC | 2sqrt(5) | 2 |
| CA | 2sqrt(2) | 1 |
Area and Perimeter
The area of Triangle ABC is:
A = (1/2)
- |(2
- 3)
- (6
- 1) + (4
- 5)| = (1/2)
- |6
- 6 + 20| = (1/2)
- |20| = 10
The perimeter of Triangle ABC is:
P = AB + BC + CA = 2sqrt(5) + 2sqrt(5) + 2sqrt(2) = 4sqrt(5) + 2sqrt(2)
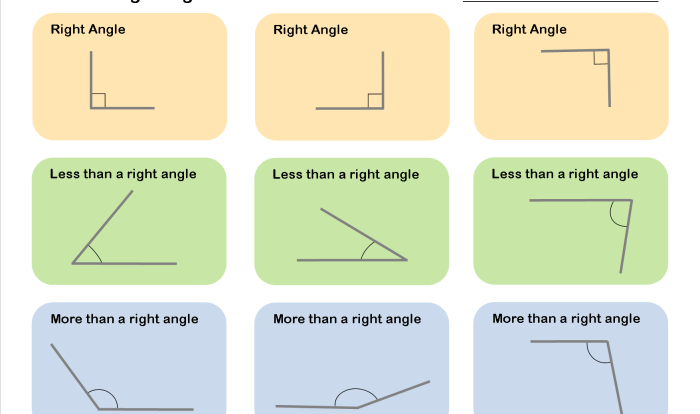
Angle Measures
The interior angles of Triangle ABC are:
- ∠A = 180° – ∠B – ∠C
- ∠B = 180° – ∠A – ∠C
- ∠C = 180° – ∠A – ∠B
The exterior angles of Triangle ABC are:
- ∠A’ = 180° – ∠A
- ∠B’ = 180° – ∠B
- ∠C’ = 180° – ∠C
Special Properties
Triangle ABC is an isosceles triangle because two of its sides are equal in length (AB = BC). It is not an equilateral triangle because all three of its sides are not equal in length. It does not satisfy the Pythagorean theorem because a^2 + b^2 ≠ c^2.
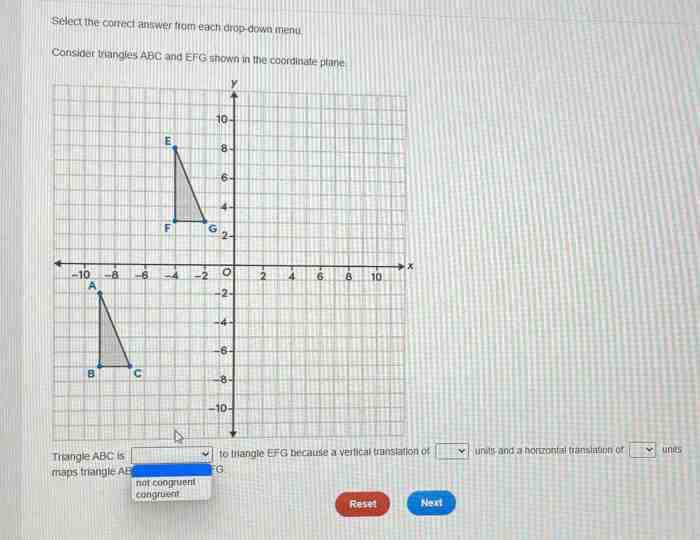
Transformations: Triangle Abc Is Shown On The Coordinate Plane
If Triangle ABC is translated 2 units to the right and 3 units up, the new coordinates of the vertices are:
- A'(4, 6)
- B'(8, 4)
- C'(6, 8)
The transformed triangle is shown on the coordinate plane below.

Answers to Common Questions
What is the distance between points A and B?
Using the distance formula, we can calculate the distance between A and B as sqrt((x2 – x1)^2 + (y2 – y1)^2), where (x1, y1) are the coordinates of point A and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of point B.
What is the slope of side AB?
The slope of side AB can be calculated using the slope formula, which is (y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1), where (x1, y1) are the coordinates of point A and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of point B.
What is the area of Triangle ABC?
The area of Triangle ABC can be calculated using Heron’s formula, which is sqrt(s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)), where s is the semiperimeter and a, b, and c are the side lengths.